GREENHOUSE-EFFECT GAS
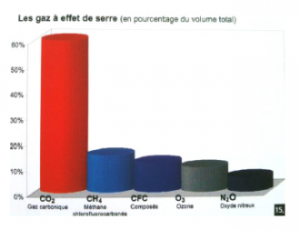
Still more greenhouse gases
Considered as the first cause of global warming, greenhouse gas emissions are not decreasing but they are increasing year by year.
If the trend is not reversed, some experts believe that the main carbon sinks of the earth will reach saturation in a few years. The greenhouse effect was discovered as early as the 19th century and described by Joseph Fourier in 1924.
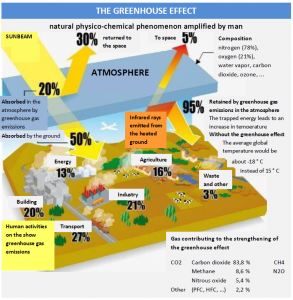
It is the phenomenon by which certain atmospheric gases absorb part of the energy of the solar radiation which is reflected by the earth and would leave without this in space.
This energy of solar radiation warms the planet. And the more gas there is, the more they cause global warming.
The priority is to reduce these greenhouse gases on the planet in order to avoid a warming of this one with as consequence:
-
Increased temperatures
-
Melting of the glaciers
-
Increase in the level of the oceans
-
Drought development